
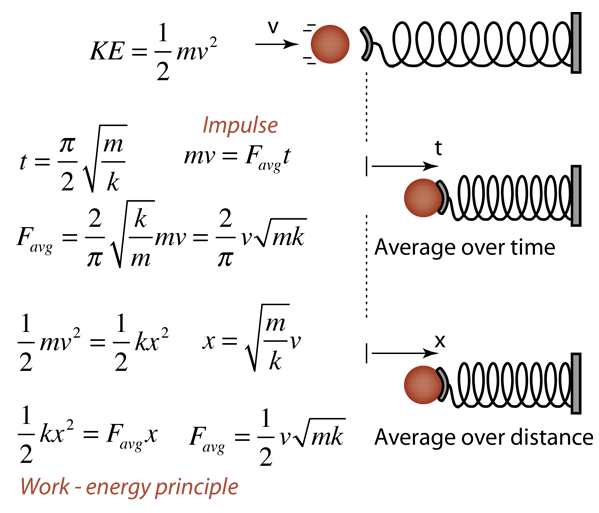
Would you be so kind as to run that by me again, but explain this a, b, c, d, in terms of initial quiescent conditions? It's essentially the linear 2nd order ODE:\begin Momentum is a physical quantity that quantifies the motion contained by a moving object, whereas impulse is a physical quantity that is utilized to gain an understanding of the change in the dynamical state of a moving particle. It seems so strange to me: as if I skirted the complexity of a nonhomogeneous differential equation (I cheated). Impulse in classical mechanics is the integral of force F, over the time interval t, due to which it acts. Would I get the same results by solving the original equation with a convolution or numerical method? Initial momentum + (integral of force over time) = Final momentumĪnd now I turn my original differential equation to thisĬan someone explain in words (sorry, I am embarrassed) what I am doing (if this is correct)? However, I cannot readily integrate this differential equation. This is a second order differential equation with a forcing function. May I ask if the following process is correct Given: Fma Apply an impulsive force using the dirac delta near 0 (with F nearly constant over the tiny impulsive interval) ma F(t) This is a second order differential equation with a forcing function. If the duration is small, then the impact of the force increases and may cause severe injury to the occupants.May I ask if the following process is correct?Īpply an impulsive force using the dirac delta near 0 (with F nearly constant over the tiny impulsive interval) If the duration is increased, then the impact of force is reduced. When the airbag inflates, it increases the duration required to stop the momentum of the passenger or the driver.

IMPULSIVE FORCE DEFINITION PHYSICS DRIVER
This reduces the force with the compartments push or pull each other, and severe jerks are avoided.Īirbags are present in cars to minimize the damage to a driver or a passenger during a collision. Hence, a smaller force is felt by the passengers traveling on the vehicle during jerks.Ĭompartments of trains are provided with buffers.īuffers increase the duration of jerks during the shunting of the train. Shock absorbents provided in the vehicles increase the duration of the jerks, thus decreasing the rate of change of momentum. Vehicles like cars, buses, and bikes are provided with shock absorbent. Thus, he exerts a smallerįorce to stop the baseball and save his hands from getting hurt.Ģ. Vehicles like cars, buses, and bikes are provided with shock absorbents. By moving his hands backward, theįielder increases the duration of making the catch. With that being said the weight can be neglected. The opposite of that is considered non impulsive. His hands experience an impulse that is equal to the product of the forceĪpplied and the time taken to catch the ball. The book we use in class describes an impulsive force in terms of certain forces acting as a very large force of short duration. The illustrations will make this statement clear.ġ. A fielder moves his hands backward while catching a baseball.Ī fielder moves his hands backward while catching a ball because, while doing so, If the time interval of an impulse is large, the force exerted will be small. J = F Δ t = m a Δ t J=F\Delta t=\text F 1 Δ t 1 = F 2 Δ t 2 .
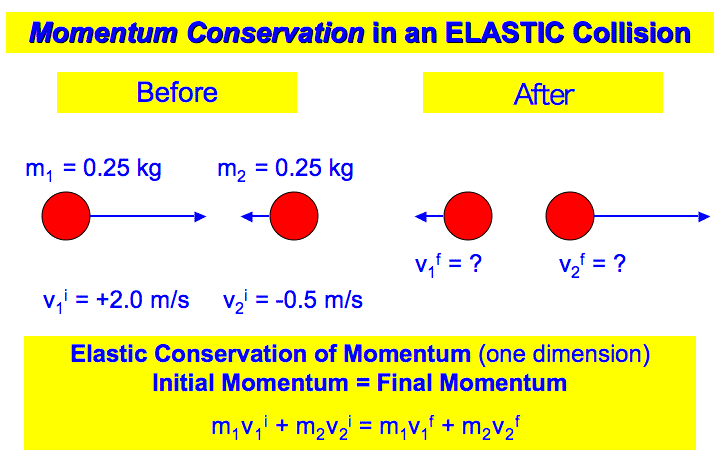
For example, if an external force is applied on a freely suspended string, then the applied force is known as impulse force only when it is large as compared to the force of gravity (weight of the string) and the tension that develops in it. The force ( F ) is said to be an impulse force if it is large as compared to the other forces present in the reference frame.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
